Applications: Linear bearings are increasingly used in various industries, including electronics, food machinery, packaging machinery, medical machinery, printing machinery, textile machinery, machinery, instrumentation, robotics, tool machinery, CNC machine tools, and automobiles, among others.
Characteristics: Low noise, low friction, high precision, and long service life. The point contact between the balls and the linear shaft results in minimal friction and high motion precision.
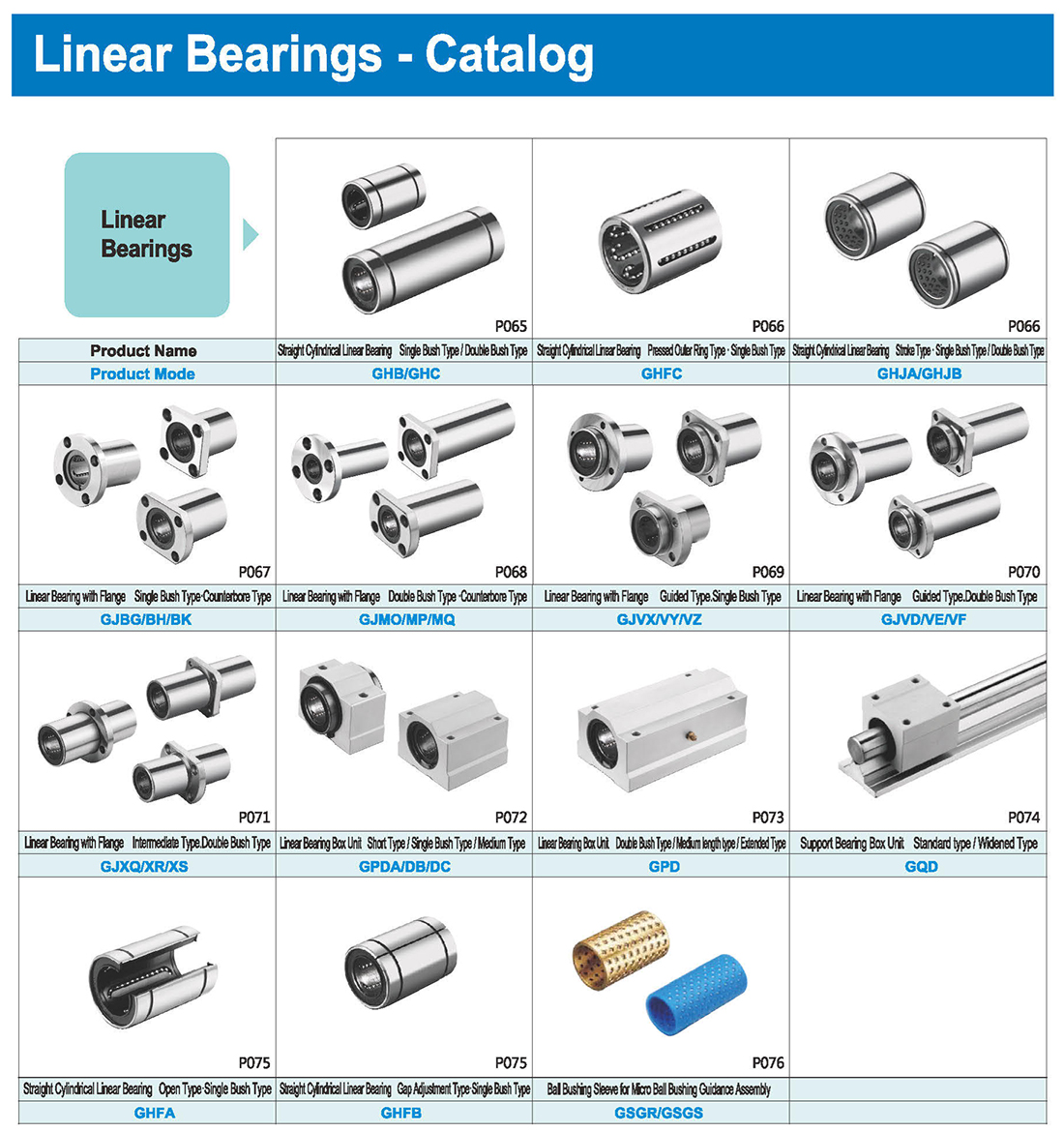
Lubrication and Dust Prevention
Bearings are coated with anti-rust oil at the factory, which does not serve as lubrication. It is recommended to clean and dry the bearing before use, and then apply lubricating grease. When applying lubricating grease, please apply it to the ball rows on the inside of the linear bearing, and then replenish it at an appropriate time.
Iron filings can significantly reduce bearing lifespan. Dust and dirt can block the retainer raceway, preventing the steel balls from rotating, leading to retainer damage and the displacement of steel balls. Bearings with seals can be used in workplaces with general dust, such as woodworking machinery and casting machinery. In such dusty environments, please add seals to both ends of the bearing to prevent dust ingress and reduce grease loss.
Compatibility
It is recommended to use linear bearings in conjunction with the guide shafts (with standard g6 tolerance) produced by our company.
Notes for Use
When installing the linear bearing into the bearing housing, auxiliary equipment should be used to avoid direct striking of the end face or sealing ring. The bearing should be evenly guided in using a buffer plate, and gently tapped to install the shaft into the linear bearing. It is important to ensure that the centerline of the shaft and bearing are aligned. External loads causing damage to the linear bearing should be evenly distributed across the entire bearing, and two or more bearings should be used. Linear bearings are not designed to withstand rotational loads, which can lead to accidents.
(1) When inserting the guide shaft into the linear bearing, please align the center and insert slowly to avoid the balls falling off or the retainer deforming.
(2) Linear bearings are not structurally suitable for rotational motion. Forced rotation may lead to unexpected accidents. Please be cautious.
(3) Linear bearings are not suitable for repeated insertion and removal.
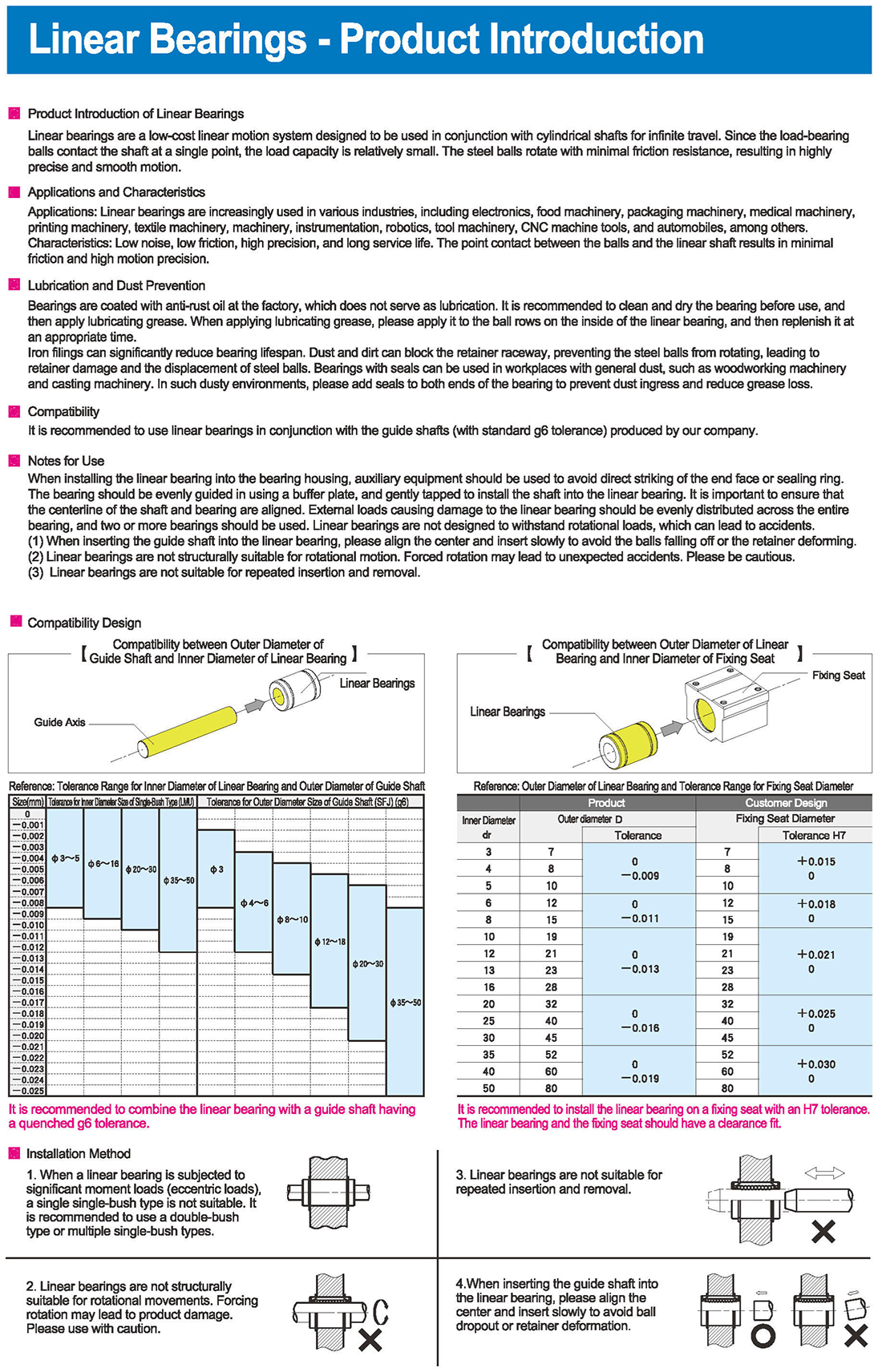
Compatibility Design
Compatibility between Outer Diameter of Guide Shaft and Inner Diameter of Linear Bearing
Compatibility between Outer Diameter of Linear Bearing and Inner Diameter of Fixing Seat
Reference: Tolerance Range for Inner Diameter of Linear Bearing and Outer Diameter of Guide Shaft
Tolerance for Inner Diameter Size of Single-Bush Type (LMU) Tolerance for Outer Diameter Size of Guide Shaft (SFJ) (g6)
Reference: Outer Diameter of Linear Bearing and Tolerance Range for Fixing Seat Diameter
Fixing Seat Product Inner Diameter Customer Design Fixing Seat Diameter Tolerance.
It is recommended to combine the linear bearing with a guide shaft having a quenched g6 tolerance.
It is recommended to install the linear bearing on a fixing seat with an H7 tolerance.
The linear bearing and the fixing seat should have a clearance fit.
Installation Method
1. When a linear bearing is subjected to significant moment loads (eccentric loads), a single single-bush type is not suitable. It is recommended to use a double-bush type or multiple single-bush types.
2. Linear bearings are not structurally suitable for rotational movements. Forcing rotation may lead to product damage. Please use with caution.
3. Linear bearings are not suitable for repeated insertion and removal.
4. When inserting the guide shaft into the linear bearing, please align the center and insert slowly to avoid ball dropout or retainer deformation.
Notes for Using Linear Bearings:
When installing the shaft, it is essential to ensure that the shaft core is parallel to the inner bore of the linear bearing, and avoid installation at improper angles.
When pressing the linear bearing into the bearing seat, do not directly hit the retaining ring or oil seal on the side end of the outer cylinder. A special tool should be used to press it in evenly.
Due to its structural characteristics, the linear bearing is only suitable for linear motion and not suitable for rotational motion. Otherwise, it may affect the service life of the linear bearing and cause unexpected accidents.
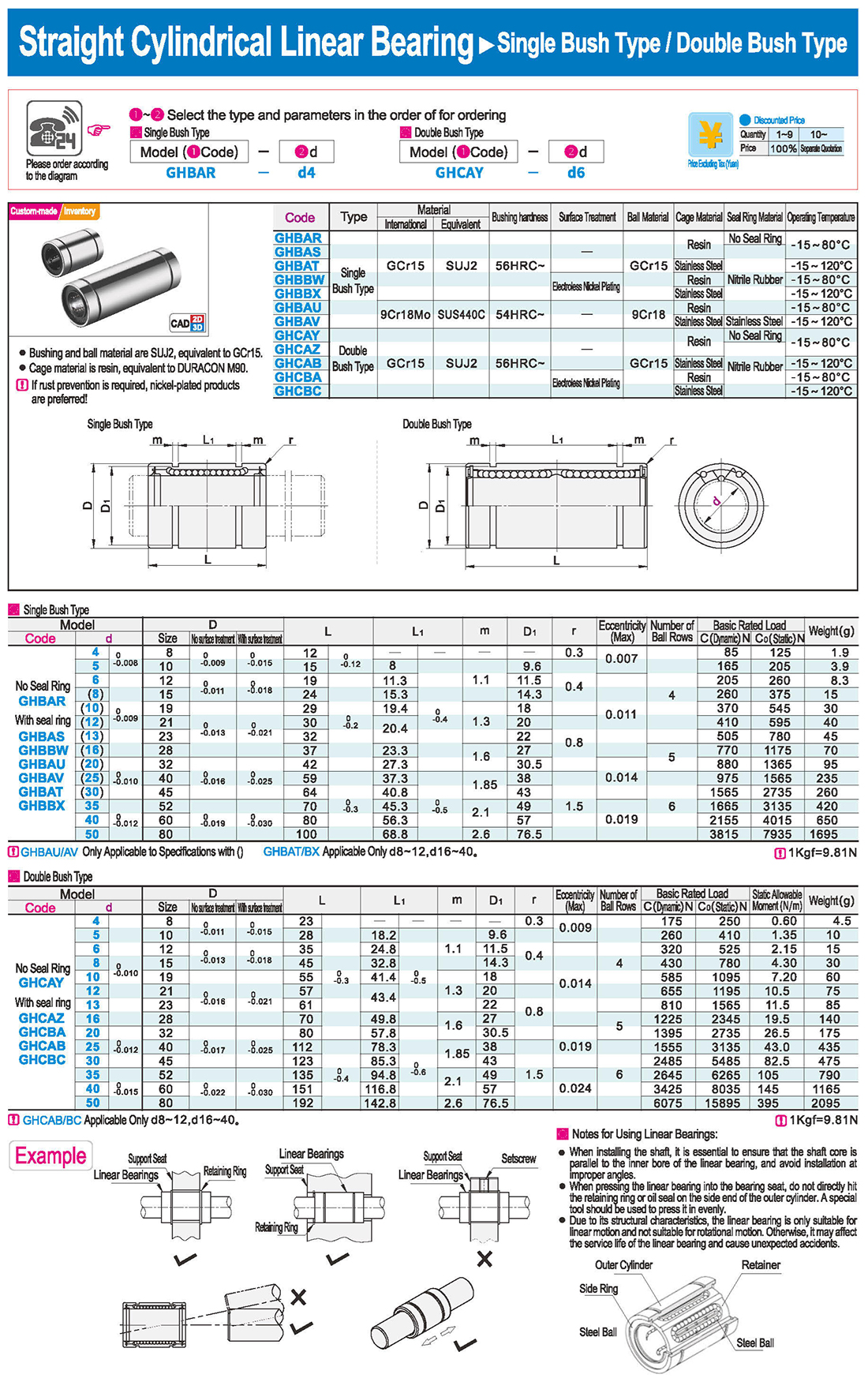
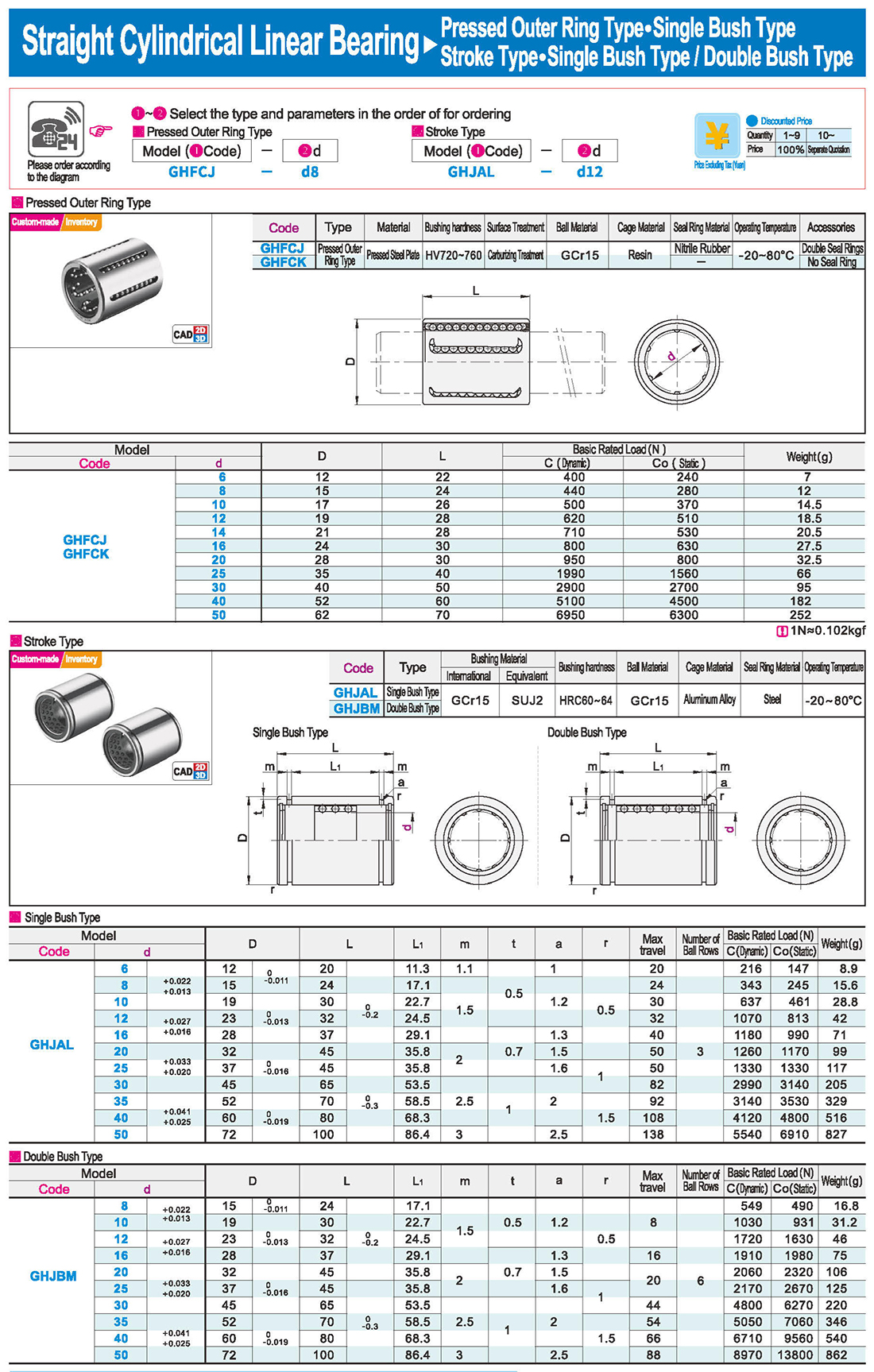
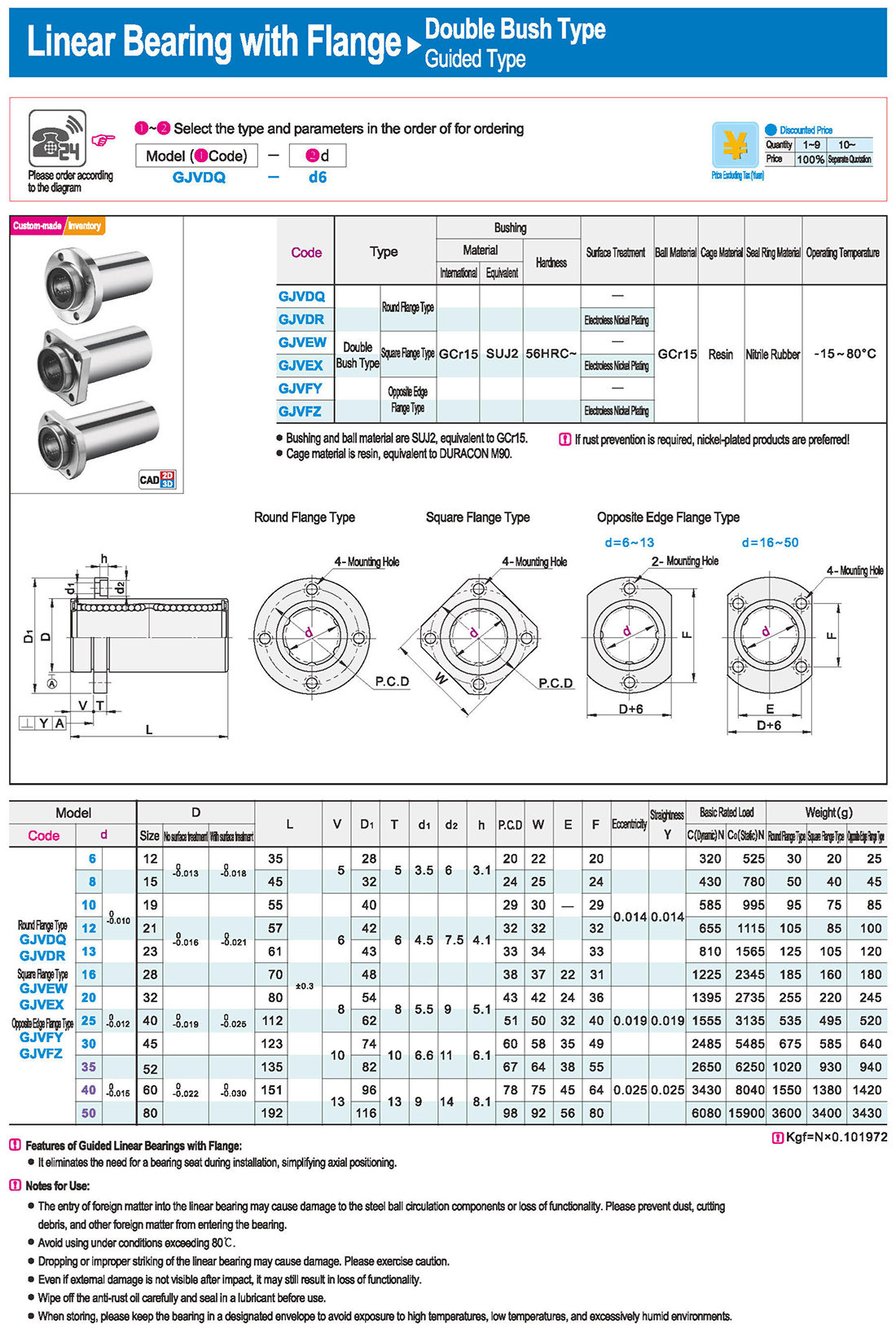
Features of Guided Linear Bearings with Flange:
● It eliminates the need for a bearing seat during installation, simplifying axial positioning.
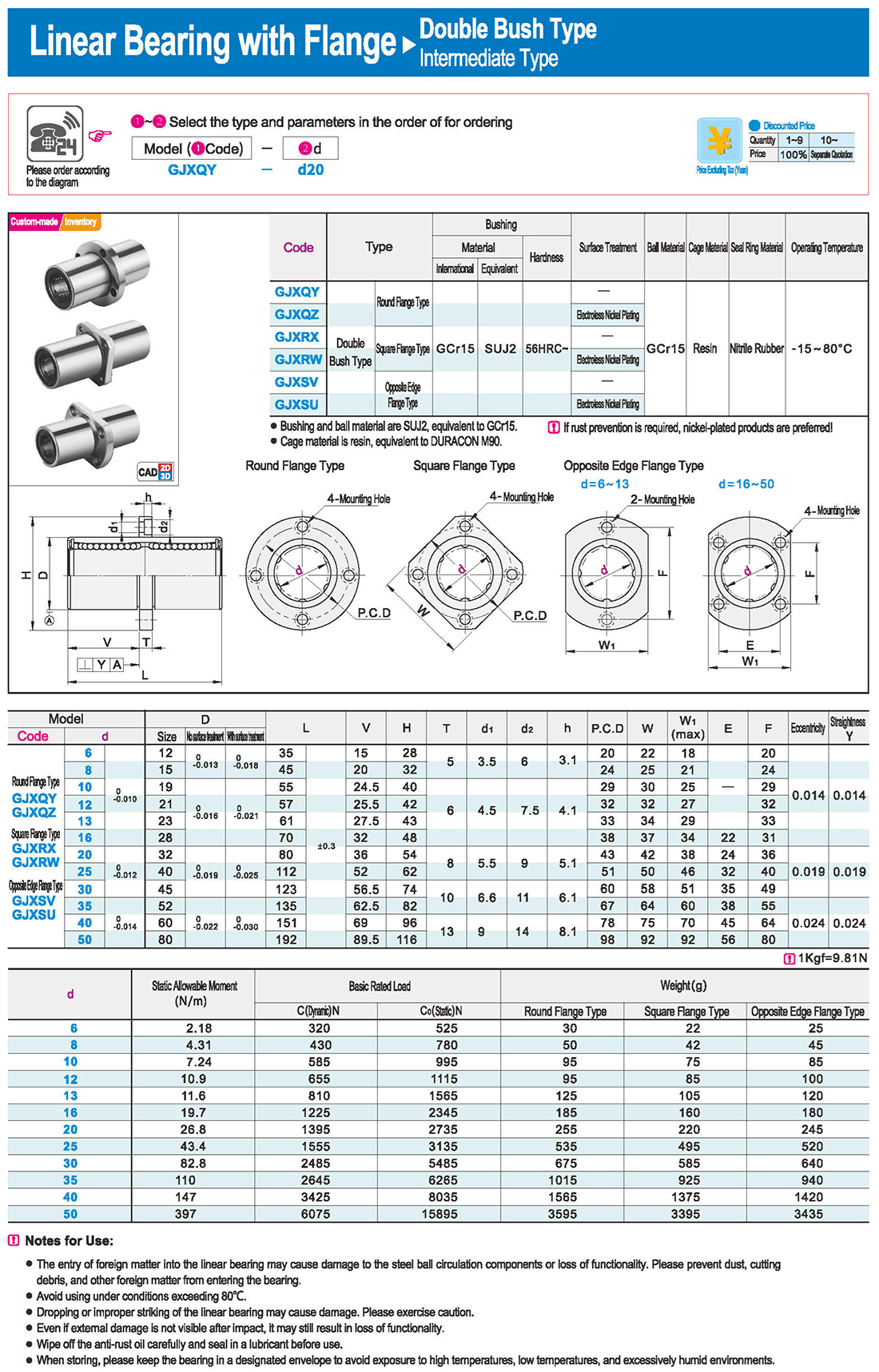
Notes for Use:
● The entry of foreign matter into the linear bearing may cause damage to the steel ball circulation components or loss of functionality. Please prevent dust, cutting debris, and other foreign matter from entering the bearing.
● Avoid using under conditions exceeding 80℃.
● Dropping or improper striking of the linear bearing may cause damage. Please exercise caution.
● Even if external damage is not visible after impact, it may still result in loss of functionality.
● Wipe off the anti-rust oil carefully and seal in a lubricant before use.
● When storing, please keep the bearing in a designated envelope to avoid exposure to high temperatures, low temperatures, and excessively humid environments.


 English
English Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Italian
Italian Arabic
Arabic Korean
Korean German
German Japanese
Japanese Vietnamese
Vietnamese Turkish
Turkish
 Introduction
Introduction Specification Table
Specification Table Download
Download









