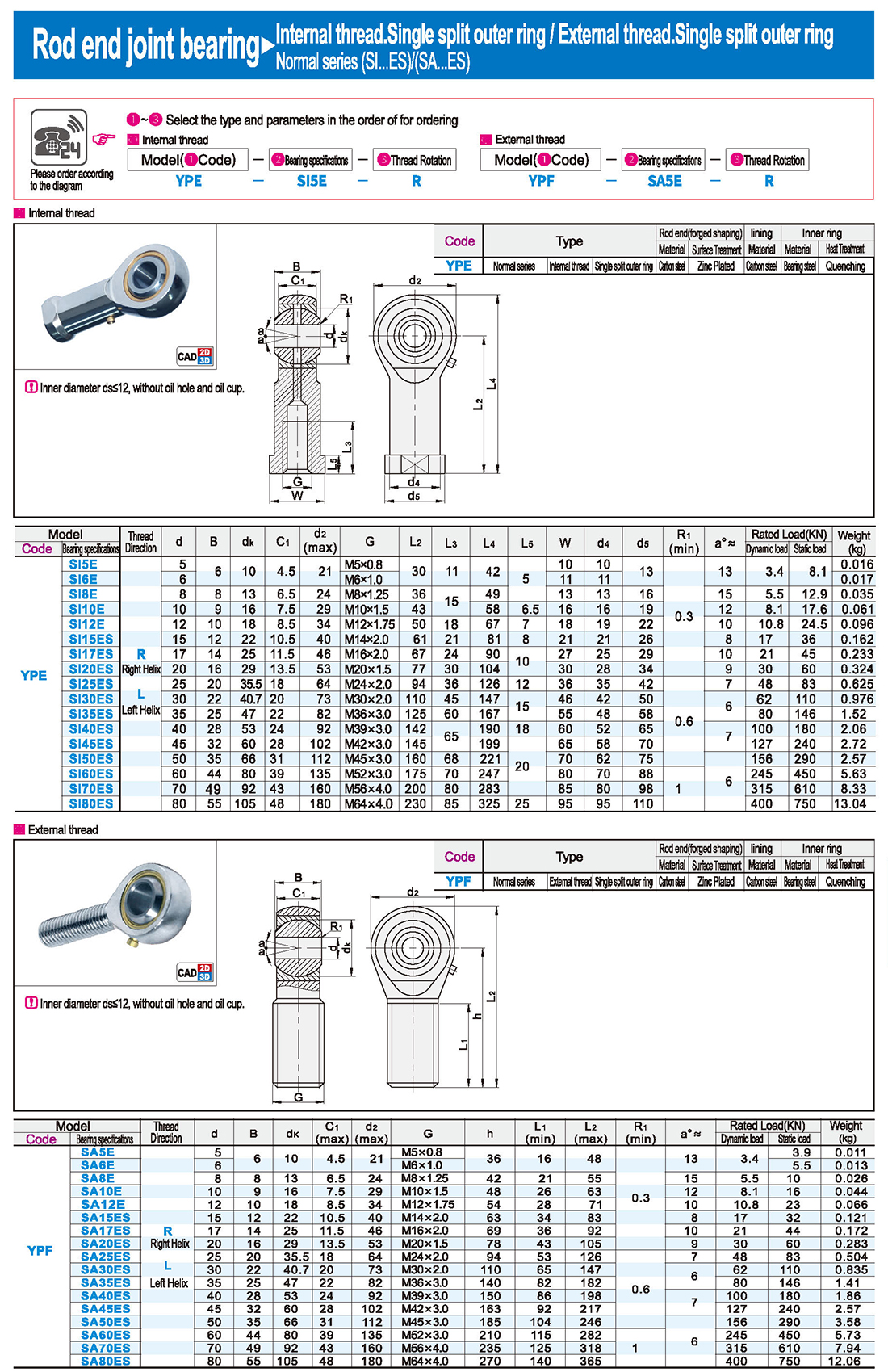
1. Strong carrying capacity
The joint bearing has a large load capacity and can withstand large radial load, axial load or radial and axial combined load. This is due to its special spherical sliding contact surface design, as well as the use of surface phosphating, galvanized, chrome or outer sliding surface lining, inserts, spraying and other special process treatment methods, which improve the strength and wear resistance of the bearing.
2. Strong adaptability
The sliding contact surface of the joint bearing is spherical, so it can be tilted in a certain Angle range (that is, aligning motion). This makes the joint bearing can still work normally when the concentricity of the supporting shaft and the shaft shell hole is large, showing a strong adaptability. In addition, the joint bearing can also withstand a certain installation error, further improving its flexibility in practical applications.
3. self-lubrication performance
Some joint bearings, such as self-lubricating joint bearings, have a sliding contact surface of the outer ring lined with a self-lubricating material. This design makes the bearing do not need to add lubricants in the work, and has the characteristics of no lubricating dirt pollution. It is especially suitable for use in the environment where the installation location is limited, the lubricant cannot be added in the work or the lubrication is afraid of pollution.
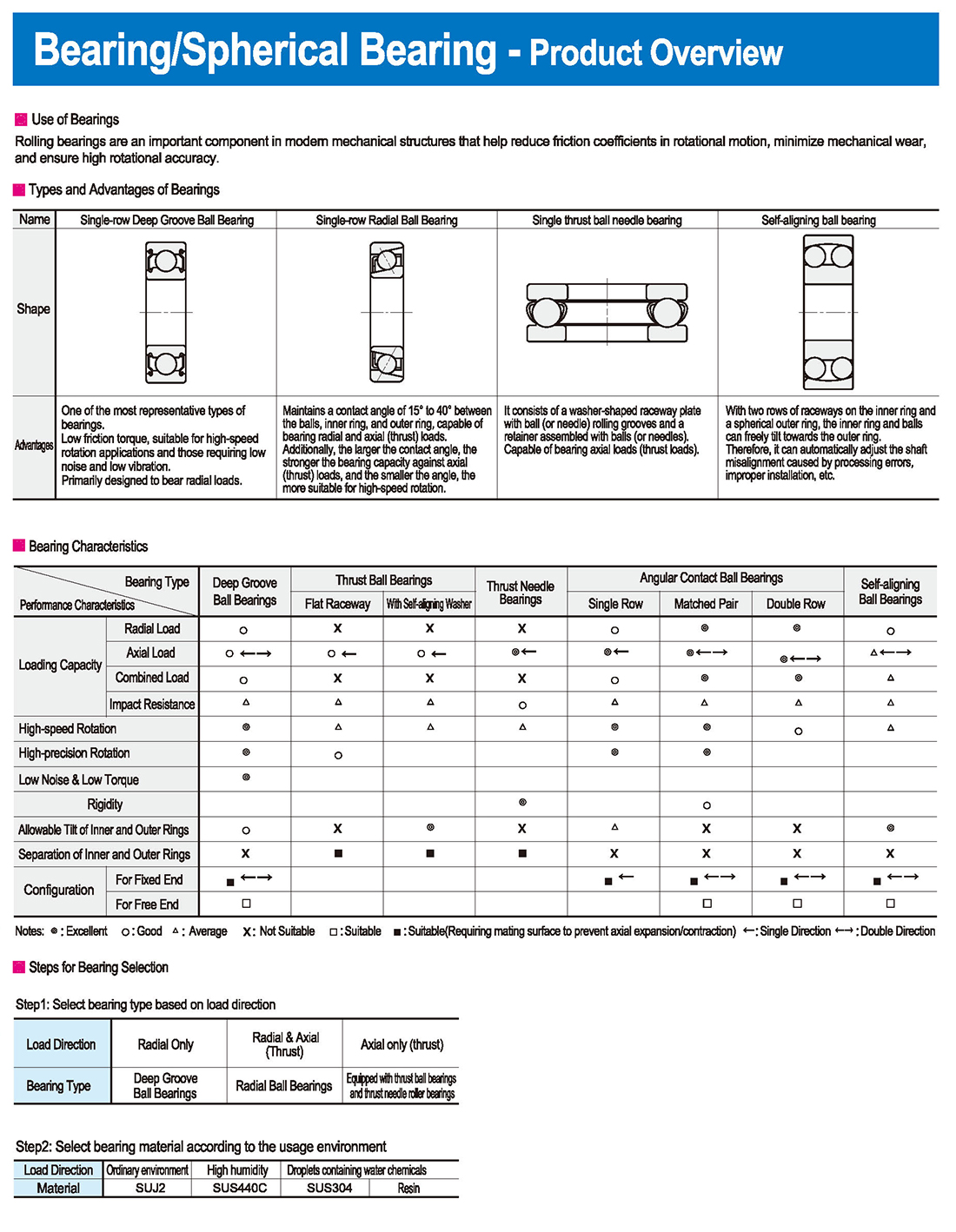
①Single-row Deep Groove Ball Bearing
One of the most representative types of bearings.
Low friction torque, suitable for high-speed rotation applications and those requiring low noise and low vibration.Primarily designed to bear radial loads.
②Single-row Radial Ball Bearing
Maintains a contact angle of 15° to 40° between the balls, inner ring, and outer ring, capable of bearing radial and axial (thrust) loads.
Additionally, the larger the contact angle, the stronger the bearing capacity against axial (thrust) loads, and the smaller the angle, the more suitable for high-speed rotation.
③Single thrust ball needle bearing
It consists of a washer-shaped raceway plate with ball (or needle) rolling grooves and a retainer assembled with balls (or needles).
Capable of bearing axial loads (thrust loads).
④Self-aligning ball bearing
With two rows of raceways on the inner ring and a spherical outer ring, the inner ring and balls can freely tilt towards the outer ring.
Therefore, it can automatically adjust the shaft misalignment caused by processing errors, improper installation, etc.


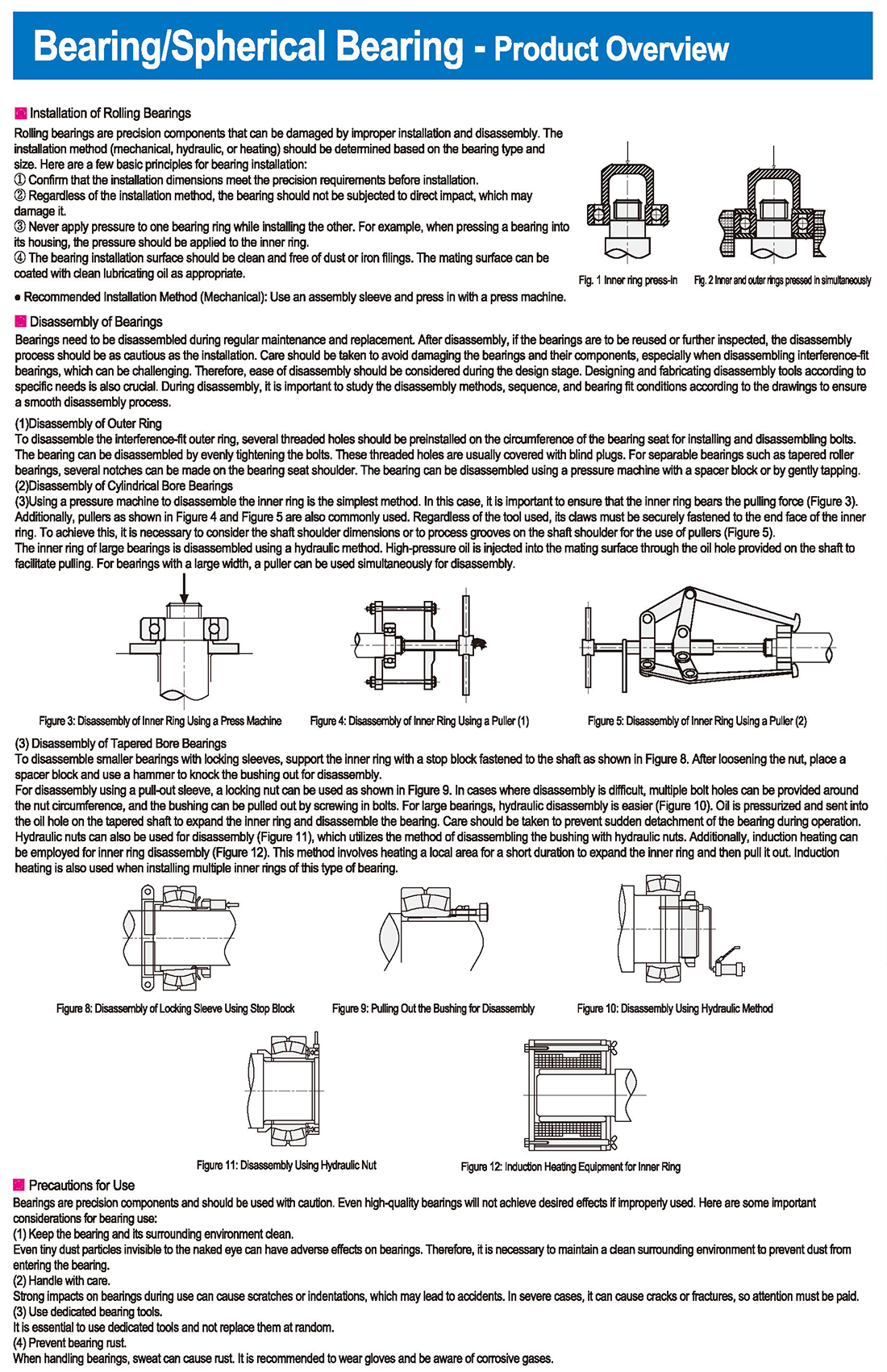
Installation of Rolling Bearings
Rolling bearings are precision components that can be damaged by improper installation and disassembly. The installation method (mechanical, hydraulic, or heating) should be determined based on the bearing type and size. Here are a few basic principles for bearing installation:
① Confirm that the installation dimensions meet the precision requirements before installation.
② Regardless of the installation method, the bearing should not be subjected to direct impact, which may damage it.
③ Never apply pressure to one bearing ring while installing the other. For example, when pressing a bearing into its housing, the pressure should be applied to the inner ring.
④ The bearing installation surface should be clean and free of dust or iron filings. The mating surface can be coated with clean lubricating oil as appropriate.
● Recommended Installation Method (Mechanical): Use an assembly sleeve and press in with a press machine.
Disassembly of Bearings
Bearings need to be disassembled during regular maintenance and replacement. After disassembly, if the bearings are to be reused or further inspected, the disassembly process should be as cautious as the installation. Care should be taken to avoid damaging the bearings and their components, especially when disassembling interference-fit bearings, which can be challenging. Therefore, ease of disassembly should be considered during the design stage. Designing and fabricating disassembly tools according to specific needs is also crucial. During disassembly, it is important to study the disassembly methods, sequence, and bearing fit conditions according to the drawings to ensure a smooth disassembly process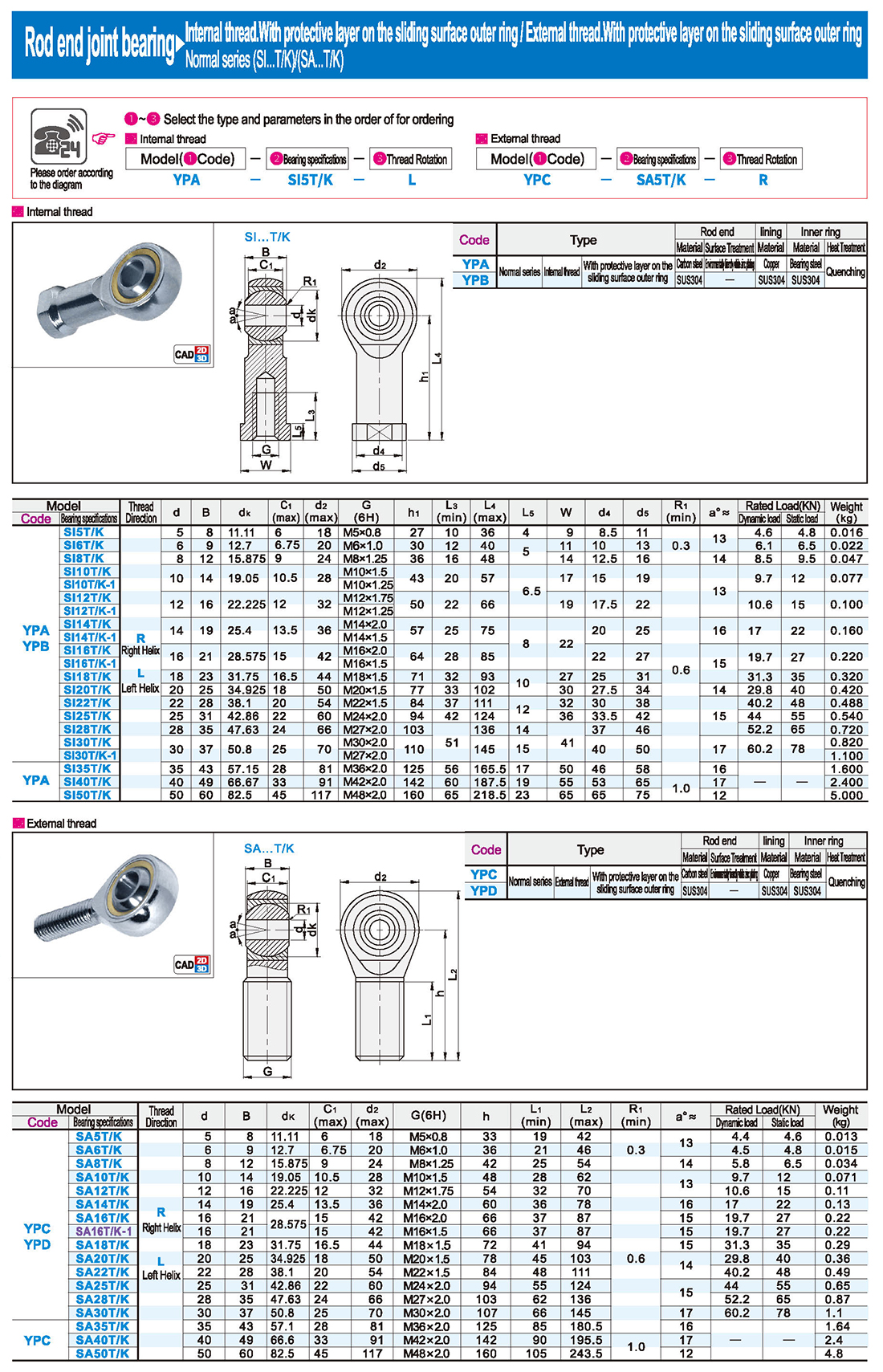


 English
English Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Italian
Italian Arabic
Arabic Korean
Korean German
German Japanese
Japanese Vietnamese
Vietnamese Turkish
Turkish
 Introduction
Introduction Specification Table
Specification Table Download
Download








